It seems like there is always some confusion concerning strings in .NET. This is both from developers who are new to the Framework and those that have been working with it for quite some time.
Strings in the .NET Framework are represented by the System.String class, which encapsulates the data manipulation, sorting, and searching methods you most commonly perform on string data.
In the .NET Framework, you can use System.String (which is the actual type name or the language alias (for C#, string). They are equivalent so use whichever naming convention you prefer but be consistent. Common usage (and my preference) is to use the language alias (string) when referring to the data type and String (the actual type name) when accessing the static members of the class.
Many mainstream programming languages (like C and C++) treat strings as a null terminated array of characters. The .NET Framework, however, treats strings as an immutable sequence of Unicode characters which cannot be modified after it has been created. Because strings are immutable, all operations which modify the string contents are actually creating new string instances and returning those. They never modify the original string data.
There is one important word in the preceding paragraph which many people tend to miss: sequence. In .NET, strings are treated as a sequence…in fact, they are treated as an enumerable sequence. This can be verified if you look at the class declaration for System.String, as seen below:
// Summary:
// Represents text as a series of Unicode characters.
public sealed class String : IEnumerable, IComparable, IComparable<string>, IEquatable<string>
The first interface that String implements is IEnumerable, which has the following definition:
// Summary:
// Exposes the enumerator, which supports a simple iteration over a non-generic
// collection.
public interface IEnumerable
{
// Summary:
// Returns an enumerator that iterates through a collection.
//
// Returns:
// An System.Collections.IEnumerator object that can be used to iterate through
// the collection.
IEnumerator GetEnumerator();
}
As a side note, System.Array also implements IEnumerable. Why is that important to know? Simply put, it means that any operation you can perform on an array can also be performed on a string. This allows you to write code such as the following:
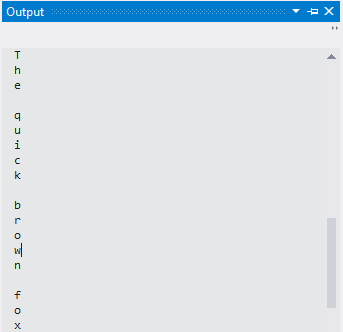
string s = "The quick brown fox";
foreach (var c in s)
{
System.Diagnostics.Debug.WriteLine(c);
}
for (int i = 0; i < s.Length; i++)
{
System.Diagnostics.Debug.WriteLine(s[i]);
}
If you executed those lines of code in a running application, you would see the following output in the Visual Studio Output window:
In the case of a string, these enumerable or array operations return a char (System.Char) rather than a string. That might lead you to believe that you can get around the string immutability restriction by simply treating strings as an array and assigning a new character to a specific index location inside the string, like this:
string s = "The quick brown fox";
s[2] = 'a';
However, if you were to write such code, the compiler will promptly tell you that you can’t do it:

This preserves the notion that strings are immutable and cannot be changed once they are created. (Incidentally, there is no built in way to replace a single character like this. It can be done but it would require converting the string to a character array, changing the appropriate indexed location, and then creating a new string.